PostgreSQL索引(3) – Hash
本文翻译自Egor Rogov的英文博客,且已征得Egor Rogov的同意。译者做了少量修改。
审校:纪昀红,中国人民大学信息学院在读博士生。
1. 结构
1.1 基本理论
很多现代编程语言都把Hash表作为一种内置的基本数据类型。从外部来看,Hash表就像普通的数组,数组的下标可以是任意的数据类型(比如,字符串),并非只能是一个整数。PG的Hash索引具有类似的结构,它是如何工作的呢?
通常来讲,一种数据类型的值域具有相当大的范围:一个text类型的列中可能会有多少个不同的字符串?但是,现实生活中,表中一个text类型的列中实际会有多个不同的值?通常情况下,并不是很多。
Hash的思想是把任意数据类型的一个值与一个整数相关联(从0到N-1,共N个值)。这个关联过程由Hash函数完成。得到的这个整数可以用作数组的下标,这个数组中存储了大量指向表中行的TID。这个数组中的元素被称作Hash表的桶 —— 一个桶中可以存储多个TID,如果相同的列值在表中不同行出现多次。
Hash函数将列值在不同的桶中分布的越均匀,则这个Hash函数越好。但是,即使是一个好的Hash函数,有时也会把不同的列值计算出相同的Hash值 —— 即发生了冲突。所以,一个桶中可能存储了不同列值的TID,因此,从Hash索引中查出的TID需要被重新检查。
随便举个例子:对字符串,我们可以使用什么Hash函数?假设桶的数量为256,我们可以用第一个字符(假设使用单字节编码)的asiic码值作为Hash值。这是一个好的Hash函数吗?当然不是:如果所有的字符串都以相同的字符开头,它们被存储到同一个桶,所有的值都需要被重新检查,Hash变得没有任何意义。假设把所有字符的asiic码值求和,再对256取模呢?这可能会好一些,但是距离预期还有很远。如果你对PG内部实现中的Hash函数感兴趣,请查看hashfunc.c中hash_any()函数的实现。
1.2 索引结构
我们回到Hash索引。对某个数据类型的一个值(索引列的值),我们的任务是快速找到它对应的TID。
当向索引中插入时,我们会对列值计算Hash值。PG中的Hash函数通常返回一个整型,它的范围大约为232 ≈ 42亿。桶的数量初始为2,随着数据量的增加而动态增加。桶的编号可以通过对Hash值做位运算得出,这个桶就是存放TID的桶。
但这还不够,因为不同的列值对应的TID可能会被存放到相同的桶中。我们应该怎么办呢?一种可能的实现方式是把原始的列值和TID一起存放在桶中,但这将大大增加索引所占的空间。因此,为了节省空间,桶中存放的是列值的Hash值,而不是直接存放列值。
当在索引中查找时,我们对列值计算Hash值,得到桶的编号。然后,遍历桶中的元素,仅返回相应Hash值得TID。这可以高效的完成,因为<Hash值, TID>被有序的存储。
然而,有时两个不同的key不仅被存储在相同的桶中,而且它们具有相同的Hash值。因此,AM会让索引引擎重新检查(索引引擎可以在检查可见性时顺便做这件事)索引条件,用来确认TID是否真的满足索引条件。
1.3 数据结构映射到页面
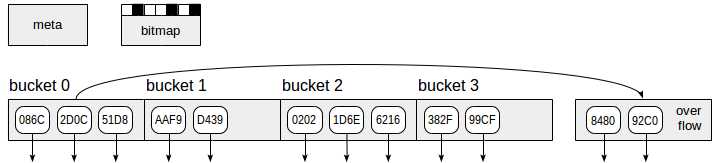
如果我们从缓冲区管理器的角度看一个索引,而不是从查询优化器和执行器的角度看,会发现所有的信息、所有的索引项都必须按一定规则存放在页面中。这样,索引页面可以被加载进缓冲区,也可以从缓冲区换出,就像管理表中的页面一样。
如上图所示,Hash索引共使用了4种页面(灰色矩形)。
- 元页面 —— 第0页,存储索引的元信息
- 桶页 —— 索引中主要的页,存储<Hash值, TID>键值对
- 溢出页 —— 和桶页的结构相同,当一个桶页的空间不够时被使用
- 位图页 —— 跟踪溢出页的使用情况,表示哪些溢出页空闲且可以被其它桶使用
索引页中向下的箭头表示TID,指向表中的行。
每次索引空间增加时,PG生成的桶数都是上次生成桶数的2倍。为了避免一次性分配大量页面,PG 10扩展空间时更加平缓。至于溢出页,则按需分配,被位图页跟踪。位图页也按需分配。
注意,Hash索引不能缩小体积。如果删除了一些索引行,已经被分配的页面不能归还给操作系统,但是可以在Vacuum之后用来存放新数据。减小索引体积的唯一方法是用reindex或vacuum full命令重建索引。
2. 示例
我们看一下Hash索引的创建。为了避免重新设计表结构,我们直接使用上篇介绍过的demo数据库,本次使用flights表。
create index on flights using hash(flight_no);
WARNING: hash indexes are not WAL-logged and their use is discouraged
CREATE INDEX
explain (costs off) select * from flights where flight_no = 'PG0001';
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on flights
Recheck Cond: (flight_no = 'PG0001'::bpchar)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on flights_flight_no_idx
Index Cond: (flight_no = 'PG0001'::bpchar)
(4 rows)
PG 9.6及之前,Hash索引中的操作都不写XLOG,请注意创建Hash索引时PG的WARNING(PG 9.5和PG 9.6两个版本会报上面的WARNING,PG 9.4不报)。这导致宕机后Hash索引不能恢复,并且不能参与复制(replication)。而且,Hash索引远不如Btree索引具有通用性,它的效率也值得怀疑。所以实际中并不值得使用这种索引。
自从PG 10开始,Hash索引已经支持XLOG,并且对内存分配做了优化,并发场景更加高效。现在创建Hash索引,也不再打印上面的WARNING。可参考下面两篇博客:PostgreSQL 10 features: Hash indexes、PostgreSQL Indexes: Hash Indexes are Faster than Btree Indexes?。
3. Hash函数
每种数据类型使用的Hash函数被存放在系统表中。
select opf.opfname as opfamily_name,
amproc.amproc::regproc AS opfamily_procedure
from pg_am am,
pg_opfamily opf,
pg_amproc amproc
where opf.opfmethod = am.oid
and amproc.amprocfamily = opf.oid
and am.amname = 'hash'
order by opfamily_name,
opfamily_procedure;
opfamily_name | opfamily_procedure
--------------------+--------------------
abstime_ops | hashint4
aclitem_ops | hash_aclitem
array_ops | hash_array
bool_ops | hashchar
bpchar_ops | hashbpchar
bpchar_pattern_ops | hashbpchar
bytea_ops | hashvarlena
char_ops | hashchar
cid_ops | hashint4
date_ops | hashint4
enum_ops | hashenum
float_ops | hashfloat4
float_ops | hashfloat8
integer_ops | hashint2
integer_ops | hashint4
integer_ops | hashint8
interval_ops | interval_hash
jsonb_ops | jsonb_hash
macaddr8_ops | hashmacaddr8
macaddr_ops | hashmacaddr
name_ops | hashname
network_ops | hashinet
numeric_ops | hash_numeric
oid_ops | hashoid
oidvector_ops | hashoidvector
pg_lsn_ops | pg_lsn_hash
range_ops | hash_range
reltime_ops | hashint4
text_ops | hashtext
text_pattern_ops | hashtext
time_ops | time_hash
timestamp_ops | timestamp_hash
timestamptz_ops | timestamp_hash
timetz_ops | timetz_hash
uuid_ops | uuid_hash
xid_ops | hashint4
(36 rows)
虽然这些函数没有在文档中说明,我们可以直接使用它们计算对应类型的Hash值。例如:
select hashtext('one');
hashtext
-----------
127722028
(1 row)
select hashtext('two');
hashtext
-----------
345620034
(1 row)
4. 属性
我们来看一下Hash索引的属性。查询语句见上一篇文章,这里直接展示结果。
name | pg_indexam_has_property
---------------+-------------------------
can_order | f
can_unique | f
can_multi_col | f
can_exclude | t
name | pg_index_has_property
---------------+-----------------------
clusterable | f
index_scan | t
bitmap_scan | t
backward_scan | t
name | pg_index_column_has_property
--------------------+------------------------------
asc | f
desc | f
nulls_first | f
nulls_last | f
orderable | f
distance_orderable | f
returnable | f
search_array | f
search_nulls | f
通过比较两个列值的Hash值的大小,无法推断出两个列值谁大谁小。因此,通常来讲,Hash索引仅支持等值查询。
select opf.opfname AS opfamily_name,
amop.amopopr::regoperator AS opfamily_operator
from pg_am am,
pg_opfamily opf,
pg_amop amop
where opf.opfmethod = am.oid
and amop.amopfamily = opf.oid
and am.amname = 'hash'
order by opfamily_name,
opfamily_operator;
opfamily_name | opfamily_operator
--------------------+------------------------------------------------------------
abstime_ops | =(abstime,abstime)
aclitem_ops | =(aclitem,aclitem)
array_ops | =(anyarray,anyarray)
bool_ops | =(boolean,boolean)
bpchar_ops | =(character,character)
bpchar_pattern_ops | =(character,character)
bytea_ops | =(bytea,bytea)
char_ops | =("char","char")
cid_ops | =(cid,cid)
date_ops | =(date,date)
enum_ops | =(anyenum,anyenum)
float_ops | =(real,real)
float_ops | =(double precision,double precision)
float_ops | =(real,double precision)
float_ops | =(double precision,real)
integer_ops | =(integer,bigint)
integer_ops | =(smallint,smallint)
integer_ops | =(integer,integer)
integer_ops | =(bigint,bigint)
integer_ops | =(bigint,integer)
integer_ops | =(smallint,integer)
integer_ops | =(integer,smallint)
integer_ops | =(smallint,bigint)
integer_ops | =(bigint,smallint)
interval_ops | =(interval,interval)
jsonb_ops | =(jsonb,jsonb)
macaddr8_ops | =(macaddr8,macaddr8)
macaddr_ops | =(macaddr,macaddr)
name_ops | =(name,name)
network_ops | =(inet,inet)
numeric_ops | =(numeric,numeric)
oid_ops | =(oid,oid)
oidvector_ops | =(oidvector,oidvector)
pg_lsn_ops | =(pg_lsn,pg_lsn)
range_ops | =(anyrange,anyrange)
reltime_ops | =(reltime,reltime)
text_ops | =(text,text)
text_pattern_ops | =(text,text)
time_ops | =(time without time zone,time without time zone)
timestamp_ops | =(timestamp without time zone,timestamp without time zone)
timestamptz_ops | =(timestamp with time zone,timestamp with time zone)
timetz_ops | =(time with time zone,time with time zone)
uuid_ops | =(uuid,uuid)
xid_ops | =(xid,xid)
(44 rows)
因此,Hash索引不能返回有序的结果(can_order、orderable)。基于相同的原因,Hash索引不处理NULL值;“相等”对NULL值来说没有意义(search_nulls)。
因为Hash索引不存储列值(仅存储列值的Hash值),因此它不支持Index Only Scan(returnable)。
Hash索引页也不支持多列索引(can_multi_col)。
5. 内部实现
从PG 10开始,可以使用pageinspect插件研究Hash索引的内部实现。
create extension pageinspect;
元页面(可以查出索引中的行数,被使用的桶的最大编号):
select hash_page_type(get_raw_page('flights_flight_no_idx',0));
hash_page_type
----------------
metapage
(1 row)
select ntuples, maxbucket
from hash_metapage_info(get_raw_page('flights_flight_no_idx',0));
ntuples | maxbucket
---------+-----------
33121 | 127
(1 row)
一个桶页(可以查出页面中live tuple和dead tuple的数量,dead tuple占用的空间可以被vacuum回收):
select hash_page_type(get_raw_page('flights_flight_no_idx',1));
hash_page_type
----------------
bucket
(1 row)
select live_items, dead_items
from hash_page_stats(get_raw_page('flights_flight_no_idx',1));
live_items | dead_items
------------+------------
407 | 0
(1 row)
如果不研究源代码,很难将所有字段的含义弄清楚。如果你愿意,你可以从这个README开始。pageinspect的文档在这里。